Motion - Introduction
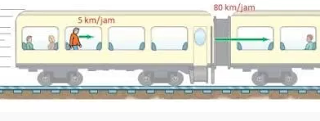
Motion is the change of position of an object observed from a reference point. The reference point is defined as the starting point of the object or the point where the observer is located.For example, you are in a train that is moving straight at a speed of 80 km / h, then you walk towards the front of the train with a speed of 5 km / hour. Your speed is 5 km / h when viewed from the observer (reference point) which is also in the train.However, if the observer is at the station or the reference point is outside the carriage, then you are considered to be moving at a speed of 80 km / h + 5 km / h = 85 km / h. (Note the picture below)
(Image Source : Douglas C, 2005)
So it is important to set a reference point when we are observing a moving object.
At the moment an object moves, the object will experience a distance change and can also experience a change in position or so-called displacement. Here is described further,
At the moment an object moves, the object will experience a distance change and can also experience a change in position or so-called displacement. Here is described further,
- Distance (distance) is the length of the entire path taken by a moving object.Distance only has value.
- The displacement is the length of the straight path measured from the initial position with the final position of the object. Switch has value and direction.
It can be concluded that, the distance only has a value so it is a scalar quantity.While the displacement is a quantity that has value and direction. Magnitudes of value and direction are called vectors and are represented as arrows. In the picture below, the blue arrow represents a displacement of 40 m in the direction to the right (East).
Speed (speed) is the comparison between the distance traveled by the object with the necessary time interval. Speed is a scalar scale (only has a value).
$$\text{speed}=\frac{\text {distance traveled}}{\text{time interval}}$$
Velocity (velocity) is the comparison between the displacement of objects with the necessary time intervals. Speed is a vector quantity (has a value and direction).
$$\text{velocity}=\frac{\text{displacement}}{\text{time interval}}=\frac{\text{last position - Begining position}}{\text{interval time}}$$
If we take the example back when you move straight 70 m to the east then walk back 30 m to the West, then the total distance you travel is 70 m + 30 m = 100 m, but the displacement you do is only 40 m. If it is assumed you are running for 70 seconds, then we can find your speed and velocity.Your Speed Is :
$$\text{speed}=\frac{\text {distance traveled}}{\text{time interval}}=\frac{\text{100 m}}{\text{70 s}}=\text{1,42 m/s}$$
Meanwhile, your Velocity is :
$$\text{velocity}=\frac{\text{displacement}}{\text{time interval}}=\frac{\text{last position - Begining position}}{\text{interval time}}=\frac{\text{40 m}}{\text{70 s}}=\text{0,57 m/s}$$
Motion Straight (GL)
Motion Straight included as Motion Translation, ie movement of an object that moves without rotating. It is called GL because the path is a straight line. For example we can see in cars that move forward, the movement of apples that fall from the tree, and on every object that moves on a straight path.This motion is divided into two types based on the presence and absence of acceleration, ie Regular Straight Motion and Straight Turned Motion .
STRONG STRAIGHT MOTION
Regular Straight Motion (GLB) is a straight motion that has a fixed speed because of the absence of acceleration on the object. Thus, the acceleration value of the object experiencing GLB is zero (a = 0).How to find the value of speed on objects that have regular GL use the same equation as described above. The following is displayed in formulas,
$$\text{v}=\frac{\text {s}}{\text{t}}$$
which means :
$$\text{velocity}=\frac{\text {scale}}{\text{time}}$$
We already know that :
v = velocity ( km / h or m/s)
s = dispacement ( m )
t = time ( s)
Example Regular Straight Circle Problem
Problem: A cyclist cycles for 2.5 hours along a straight path. What is the distance traveled if known speed of 18 km / hour?Solution :
the velocity formula is $$\text{v}=\frac{\text {s}}{\text{t}}$$
so we can write that $$\text{s}=\text {v}\times\text{t}$$
$$\text{s}=\text {18 km/h}\times\text{2,5 h}=\text{45 km}$$
So, the cyclist has traveled a distance of 45 km.

0 Response to "Motion Straight - Understanding, Formula, & Example Regular Straight Circle Problem"
Posting Komentar